Setting up Azure API Permissions
This guide explains how to configure PIM+ API permissions for Microsoft Intune, Microsoft Teams, and Windows Defender in Azure. Follow these steps to ensure that your application has the necessary permissions to operate effectively.
Prerequisites
- An active Azure account.
- Access to Azure Portal with administrative privileges.
- Basic understanding of Azure services and API management.
In Azure, authentication requires more than just a username and password. You'll also need an Azure authentication profile for each Azure-enabled event monitor you want to use in PIM+.
Step 1: Register an Application
-
Log in to the Azure portal and select "Subscriptions" from the list of Azure services.
-
Next, record your subscription ID in the appropriate field.
-
For the next step, go to All Services, then navigate to Azure Active Directory. There, select App Registrations.

-
Select New registration.
- Choose the user-facing name for the new registration. You will have the opportunity to change this later if needed.
- Once you've chosen the name, click Register.
- Next, record the Application (client) ID and the Directory (tenant) ID.

- Under Client credentials, select Add a certificate or secret.
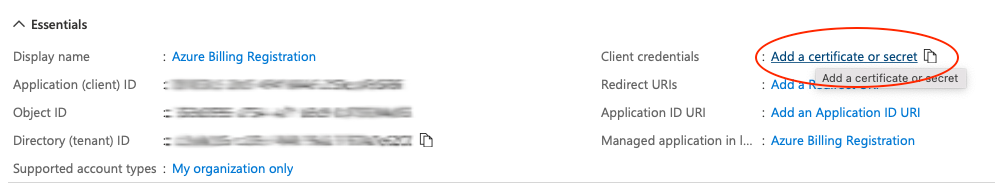
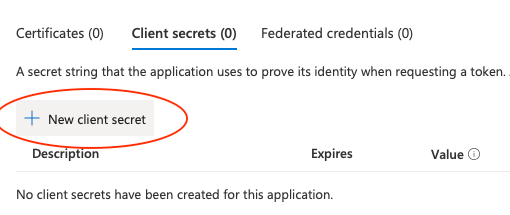
- Choose New Client Secret.
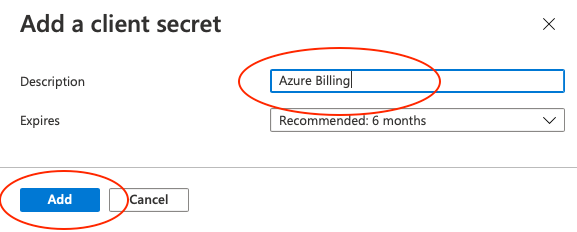
- Choose a name for the certificate, then click Add.
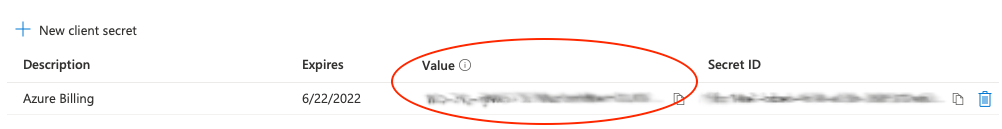
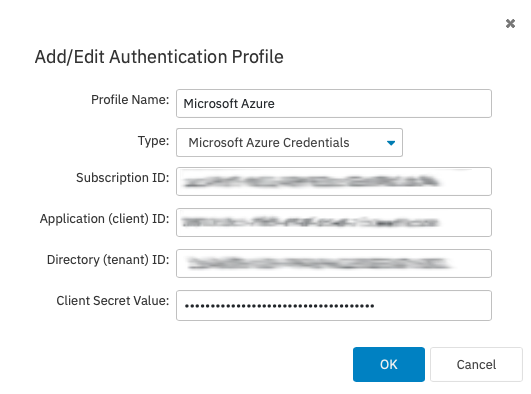
Back in PIM+, you can now create a new profile in Settings > Authentication Profiles that will be used to authenticate with your Azure event monitors. Add the subscription ID, application ID, directory ID, and the client secret value in the fields you see below.
Step 2: Configure API Permissions
After registering your application, configure API permissions for Microsoft Graph, which includes Microsoft Intune, Teams, and Windows Defender.
General Steps
- Navigate to your application page in the Azure portal.
- Select API permissions > Add a permission.
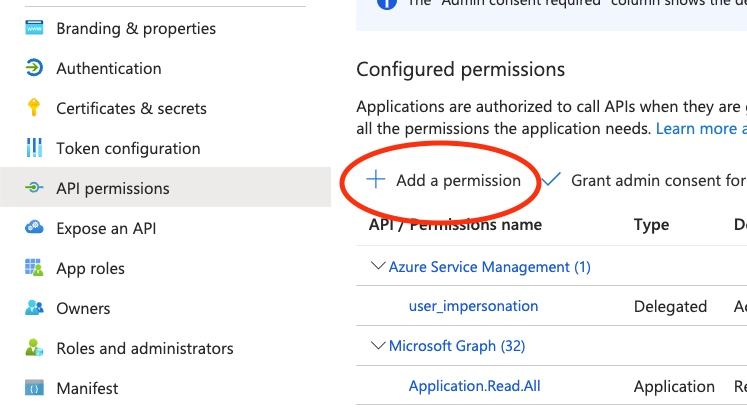
- Choose Microsoft APIs, then select Microsoft Graph.

- Choose Application permissions.
Specific Permissions
Microsoft Azure (Mandatory)
- User.Read.All: Allows reading all users’ full profiles.
- Organization.Read.All: Allow to read the Organization content.
- Application.Read.All: Read all applications.
- AuditLog.Read.All: Read the audit log.
Microsoft 365
- LicenseAssignment.ReadWrite.All: Tracks and manages license usage for Microsoft 365.
- ServiceHealth.Read: Assesses the health of Microsoft 365 services associated with your account.
Microsoft Intune
- DeviceManagementApps.Read.All: Allows reading Microsoft Intune Apps.
- DeviceManagementManagedDevices.Read.All: Allows reading Microsoft Intune Devices.
- DeviceManagementConfiguration.Read.All: Allow to read the device configuration.
Microsoft Teams
- Channel.ReadBasic.All: Read the names and descriptions of all channels.
- ChannelMember.Read.All: Read the members of all channels.
- ChannelMessage.Read.All: Read all channel messages.
- ChannelSettings.Read.All: Read the names, descriptions, and settings of all channels.
- GroupMember.Read.All: Read all group memberships.
- Team.ReadBasic.All: Get a list of all teams.
- TeamMember.Read.All: Read the members of all teams.
- TeamsActivity.Read.All: Read all users' teamwork activity feed.
- TeamSettings.Read.All: Read all teams' settings.
Setting up Windows Defender ATP
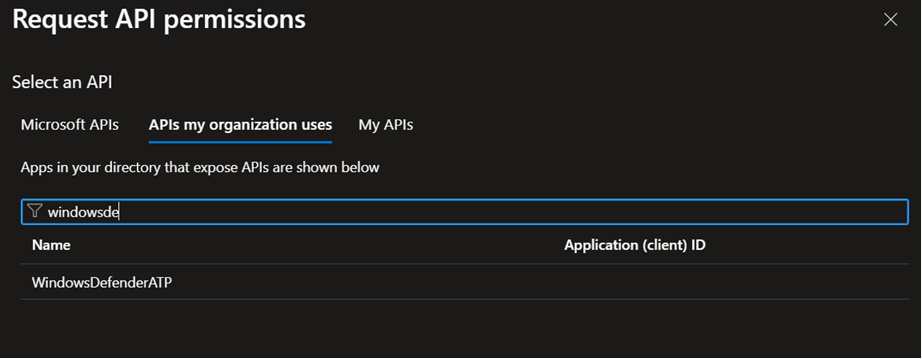
Windows Defender
- Machine.Read.All: Allows reading all machine profiles.
- SecurityRecommendation.Read.All: Allows reading Threat and Vulnerability security recommendations.
- Vulnerability.Read.All: Allows reading Threat and Vulnerability Management vulnerability information.
Step 3: Grant Admin Consent
- After adding permissions, navigate to Grant admin consent and click it.
- Confirm by selecting Yes.
Final Steps
After configuring all the necessary permissions and granting admin consent, ensure to:
- Configure any additional settings specific to your application’s needs.
- Test the application to confirm that it has the necessary access to Azure services.
- Consider adding a troubleshooting section for common issues that may arise during the setup process.
By following this guide and adding appropriate visual aids, your application will be well-prepared to interact with Microsoft Intune, Teams, and Windows Defender through the Azure API.